AP Human Geography Unit 5 FRQ delves into the captivating realm of human population dynamics, migration, and urbanization, providing a comprehensive understanding of the intricate interplay between humans and their environments.
From examining the factors driving population growth to analyzing the challenges and opportunities associated with urbanization, this unit offers a multifaceted exploration of the human experience and its profound impact on the world around us.
Key Concept: Human Population Dynamics
Population dynamics encompass the intricate interplay of factors that shape human population size, distribution, and growth. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for addressing global challenges and ensuring sustainable development.
Factors Influencing Population Growth
- Fertility Rate:The average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years. High fertility rates contribute to rapid population growth.
- Mortality Rate:The number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a population. Decreasing mortality rates, often due to improved healthcare and nutrition, lead to population growth.
- Migration:The movement of people into or out of a region. Immigration can increase population size, while emigration reduces it.
Challenges of Rapid Population Growth
Uncontrolled population growth can strain resources, exacerbate environmental degradation, and hinder sustainable development:
- Resource Depletion:Growing populations demand more food, water, and energy, putting pressure on finite resources.
- Environmental Degradation:Population growth often leads to increased pollution, deforestation, and habitat loss, threatening ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Economic and Social Issues:Rapid population growth can strain infrastructure, housing, and employment opportunities, leading to poverty, inequality, and social unrest.
Environmental Impacts of Population Growth
- Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Larger populations consume more energy, leading to increased emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
- Deforestation:As populations grow, they require more land for agriculture, housing, and infrastructure, often leading to the clearing of forests, reducing biodiversity and exacerbating climate change.
- Water Scarcity:Growing populations put pressure on water resources, as more people compete for limited water supplies, potentially leading to conflicts and water shortages.
Human Migration
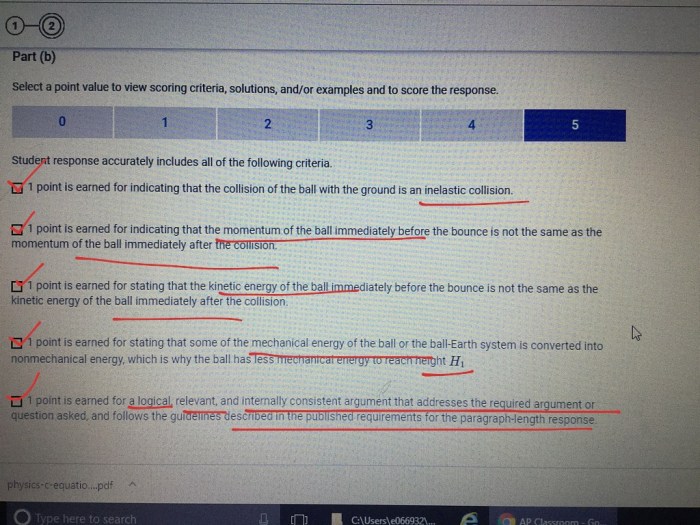
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another, either within a country or across borders. It can be temporary or permanent, and it can be voluntary or forced. Migration has a long history, and it has played a major role in shaping the world’s population distribution.
There are many different types of migration. Some people migrate for economic reasons, such as to find a better job or to escape poverty. Others migrate for political reasons, such as to escape war or persecution. Still others migrate for environmental reasons, such as to escape natural disasters or climate change.
The factors that drive people to migrate are complex and varied. Some of the most common factors include:
- Economic factors:People often migrate to find better economic opportunities, such as higher wages, better jobs, or more affordable housing.
- Political factors:People may migrate to escape war, persecution, or other forms of political instability.
- Environmental factors:People may migrate to escape natural disasters, such as floods, droughts, or earthquakes. They may also migrate to escape the effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels or extreme weather events.
- Social factors:People may migrate to be closer to family or friends, or to find a community that shares their values or beliefs.
Migration can have a significant impact on both the sending and receiving countries. In the sending country, migration can lead to a loss of population, which can have a negative impact on the economy and the social fabric of the community.
In the receiving country, migration can lead to an increase in population, which can put a strain on resources and services.
Migration can also have a positive impact on both the sending and receiving countries. In the sending country, migration can lead to remittances, which can help to improve the economy. In the receiving country, migration can lead to a more diverse population, which can bring new skills and ideas to the community.
Urbanization
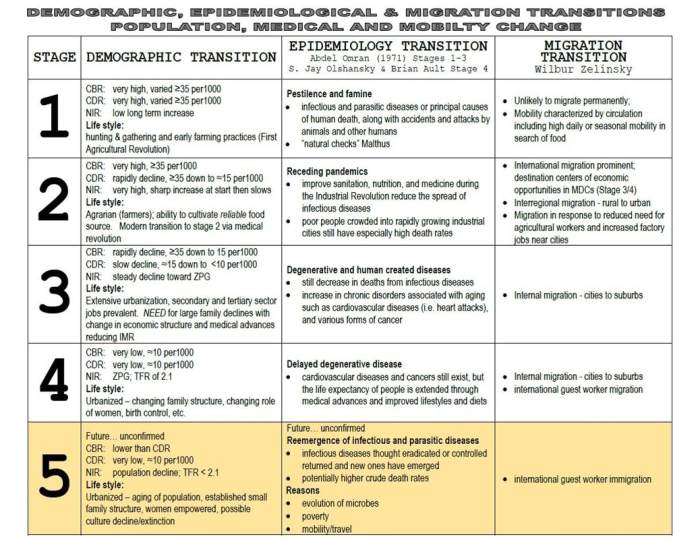
Urbanization refers to the process by which people move from rural areas to cities. This phenomenon has been occurring at an accelerating rate in recent decades, with the world’s urban population now exceeding its rural population. Urbanization is driven by a variety of factors, including economic opportunities, better education and healthcare, and the desire for a more cosmopolitan lifestyle.
Types of Urban Settlements
Urban settlements can be classified into several types, based on their size, function, and location. The largest urban settlements are known as megacities, which have populations of over 10 million people. Other types of urban settlements include large cities, medium-sized cities, small cities, towns, and villages.
Challenges and Opportunities of Urbanization
Urbanization offers both challenges and opportunities for societies. On the one hand, cities can be engines of economic growth and innovation. They provide a concentration of human capital, which can lead to new ideas and businesses. Cities also offer a wider range of cultural and recreational opportunities than rural areas.
On the other hand, urbanization can also lead to a number of problems, including overcrowding, pollution, and crime. Cities can also be more expensive to live in than rural areas. As a result, it is important for governments to plan for the challenges of urbanization in order to maximize its benefits and minimize its negative impacts.
Economic Development

Economic development refers to the long-term increase in the economic well-being of a country or region. It involves a complex interplay of factors that contribute to sustained economic growth and improved living standards.
Models of Economic Development
Various models have been proposed to explain the process of economic development:
- Rostow’s Stages of Growth Model: Proposes five stages of economic development, from traditional society to high mass consumption.
- Harrod-Domar Model: Emphasizes the role of investment and capital accumulation in economic growth.
- Solow Growth Model: Highlights the role of technological progress and human capital in long-term economic growth.
Key Indicators of Economic Development
Economic development is measured using a range of indicators:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Total value of goods and services produced within a country.
- Gross National Income (GNI): Total income earned by a country’s residents, regardless of location.
- Human Development Index (HDI): Composite index that measures life expectancy, education, and income.
Factors Contributing to Economic Growth
Economic growth is influenced by a multitude of factors:
- Investment in Physical Capital: Infrastructure, machinery, and equipment.
- Investment in Human Capital: Education, healthcare, and training.
- Technological Progress: Innovations and advancements that increase productivity.
- Natural Resources: Availability and exploitation of natural resources.
- Government Policies: Fiscal, monetary, and trade policies that promote economic growth.
Cultural Geography
Culture encompasses the shared beliefs, values, customs, and behaviors that define a particular group of people. It influences every aspect of human life, from the way we communicate to the way we interact with our environment.
The components of culture include:
- Symbols:Objects, gestures, or words that carry shared meanings within a culture.
- Values:Beliefs about what is good or bad, right or wrong, that guide behavior.
- Norms:Expectations about how people should behave in different situations.
- Language:A system of communication that allows people to share ideas and experiences.
- Technology:Tools, knowledge, and techniques that people use to adapt to their environment.
Culture shapes human behavior and interactions in profound ways. It influences our perceptions, attitudes, and decision-making. It also affects how we communicate, cooperate, and resolve conflicts.
Factors Contributing to Cultural Diversity
Cultural diversity arises from a variety of factors, including:
- Geography:Different environments pose different challenges and opportunities, leading to the development of distinct cultures.
- History:Past events, such as wars, migrations, and colonialism, can shape cultural identity.
- Social structure:The organization of society, including factors such as class, gender, and ethnicity, can influence cultural norms and values.
- Technology:New technologies can introduce new ideas and practices, leading to cultural change.
- Globalization:Increased interconnectedness between different parts of the world can lead to the spread of cultural influences.
Political Geography
Political geography is the study of the relationship between politics and geography. It examines how political power is distributed and exercised over territory, and how this relationship shapes the physical and human landscapes.
Political geography encompasses a wide range of topics, including:
- The distribution of political power
- The organization of political systems
- The relationship between politics and territory
- The impact of political decisions on the environment and society
Types of Political Systems, Ap human geography unit 5 frq
There are many different types of political systems, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of political systems include:
- Autocracy:A government in which one person has absolute power.
- Oligarchy:A government in which a small group of people have power.
- Democracy:A government in which the people have power.
- Republic:A government in which the people elect representatives to make decisions for them.
- Federation:A government in which power is divided between a central government and regional governments.
Factors Influencing Political Power and Territorial Control
A variety of factors can influence political power and territorial control, including:
- Geography:The physical features of a region can influence its political power and territorial control. For example, a region with a strong military can use its geography to defend its territory from attack.
- Economics:The economic resources of a region can influence its political power and territorial control. For example, a region with a strong economy can use its wealth to build up its military and expand its territory.
- Culture:The culture of a region can influence its political power and territorial control. For example, a region with a strong sense of national identity can be more difficult to conquer than a region with a weaker sense of national identity.
- History:The history of a region can influence its political power and territorial control. For example, a region that has been conquered in the past may be more likely to be conquered again in the future.
Agricultural Systems
Agriculture, the cultivation of crops and rearing of livestock, forms the backbone of human civilization, providing sustenance and shaping societies across the globe. Agricultural systems, the methods and practices employed in food production, vary widely based on factors such as climate, technology, and cultural traditions.
Subsistence Agriculture
Subsistence agriculture, the oldest and most basic agricultural system, is practiced by small-scale farmers who primarily produce food for their own consumption and local markets. This system relies on manual labor and traditional farming techniques, with limited mechanization or chemical inputs.
Commercial Agriculture
Commercial agriculture, also known as industrial agriculture, is characterized by large-scale production of crops and livestock for profit. This system employs advanced technology, mechanization, and chemical inputs to maximize yields and meet the demands of global markets.
The AP Human Geography Unit 5 FRQ can be a bit overwhelming, but there are resources available to help you succeed. One helpful resource is the ABC Book for Romeo and Juliet , which provides a comprehensive overview of the play’s themes, characters, and plot.
By utilizing this resource, you can gain a deeper understanding of the material and prepare more effectively for the exam. Additionally, practice questions and mock exams can further enhance your preparation for the AP Human Geography Unit 5 FRQ.
Pastoralism
Pastoralism, a nomadic or semi-nomadic agricultural system, involves the herding of livestock in search of grazing land. This system is common in arid and semi-arid regions where crop cultivation is challenging.
Factors Influencing Agricultural Productivity
Agricultural productivity, the amount of food produced per unit of land or labor, is influenced by several factors:
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight affect crop growth and livestock productivity.
- Soil Quality: Fertile soils with adequate drainage and nutrients support healthy plant growth.
- Labor: Availability of skilled labor and efficient farming practices contribute to increased productivity.
- Capital: Investments in infrastructure, equipment, and research and development boost agricultural output.
li>Technology: Advanced machinery, irrigation systems, and biotechnology enhance yields and efficiency.
Challenges in Food Production and Distribution
Despite advancements in agricultural technology, food production and distribution face significant challenges:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and water scarcity threaten crop yields and livestock health.
- Population Growth: Increasing demand for food puts pressure on agricultural systems to produce more with limited resources.
- Food Waste: A significant portion of food produced is wasted due to spoilage, transportation inefficiencies, and consumer behavior.
- Unequal Distribution: Food distribution systems often fail to reach marginalized communities, leading to hunger and malnutrition.
- Environmental Degradation: Intensive agricultural practices can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and biodiversity loss.
Industrialization
Industrialization refers to the transition of a society from an agrarian-based economy to one dominated by manufacturing and industry. It involves the adoption of new technologies, the growth of cities, and the rise of a capitalist economy.The causes of industrialization are complex and varied, but some of the most important include:
- Technological innovations: The development of new machines and technologies, such as the steam engine and the cotton gin, made it possible to produce goods more efficiently and in larger quantities.
- Availability of resources: Industrialization requires access to raw materials, such as coal and iron ore, as well as a workforce that is willing and able to work in factories.
- Economic factors: Industrialization is often driven by the desire for economic growth and the accumulation of wealth.
Stages of Industrialization
Industrialization typically occurs in several stages:
- Pre-industrialization: This stage is characterized by a predominantly agrarian economy, with most people working in agriculture.
- Early industrialization: This stage is marked by the introduction of new technologies and the growth of manufacturing industries.
- Advanced industrialization: This stage is characterized by the dominance of heavy industry and the emergence of new technologies, such as electricity and the internal combustion engine.
- Post-industrialization: This stage is characterized by the decline of manufacturing industries and the rise of the service sector.
Impacts of Industrialization
Industrialization has had a profound impact on societies around the world. Some of the most significant impacts include: Social impacts: Industrialization has led to the growth of cities, the rise of a working class, and the decline of traditional social structures.
Economic impacts: Industrialization has led to increased economic growth, but it has also led to increased inequality and the exploitation of workers. Environmental impacts: Industrialization has led to increased pollution and environmental degradation.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability refers to the ability of the environment to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses the preservation, conservation, and restoration of natural resources, as well as the reduction of pollution and waste.Environmental
sustainability is crucial for the well-being of both humans and the planet. It ensures that we have access to clean air, water, and land, which are essential for our survival. It also protects biodiversity and ecosystem services, which provide us with food, medicine, and other resources.
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world’s countries and peoples. It involves the exchange of goods, services, ideas, and people across national borders.The causes of globalization include advances in transportation and communication technologies, the rise of multinational corporations, and the liberalization of trade and investment policies.
Dimensions of Globalization
Globalization has multiple dimensions, including:*
-*Economic globalization
The integration of national economies through trade, investment, and financial flows.
-
-*Political globalization
The increasing cooperation and interdependence among governments and international organizations.
-*Social globalization
The spread of ideas, values, and lifestyles across cultures.
-*Cultural globalization
The exchange and mixing of cultural practices and products.
-*Environmental globalization
The global interconnectedness of environmental issues, such as climate change and pollution.
Impacts of Globalization
Globalization has significant impacts on the economy, society, and the environment:
Economic Impacts
* Increased trade and investment
- Creation of global markets
- Economic growth and job creation
- Increased competition and job displacement
Social Impacts
* Spread of ideas and values
- Increased cultural diversity
- Improved access to education and healthcare
- Increased migration and displacement
Environmental Impacts
* Increased pollution and resource consumption
- Deforestation and loss of biodiversity
- Climate change and global warming
- Transboundary environmental issues
FAQ Corner: Ap Human Geography Unit 5 Frq
What are the key factors influencing population growth?
Birth rates, death rates, and migration rates are the primary factors that shape population growth.
How does rapid population growth impact the environment?
Rapid population growth can strain natural resources, increase pollution, and contribute to deforestation and other environmental challenges.
What are the different types of migration?
Migration can be classified into internal migration (within a country) and international migration (across borders). It can also be voluntary or forced, and temporary or permanent.