Types of figurative language chart – Embark on an exploration of figurative language, a literary tool that breathes life into words, enhancing our ability to express complex ideas and emotions. This comprehensive chart unveils the nuances of simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, and irony, empowering you to master the art of crafting vivid and impactful language.
As we delve into each type of figurative language, we’ll uncover its unique characteristics, explore its evocative power, and discover how it can elevate your writing to new heights. Get ready to unlock the secrets of language and unleash your imagination.
Types of Figurative Language: Types Of Figurative Language Chart
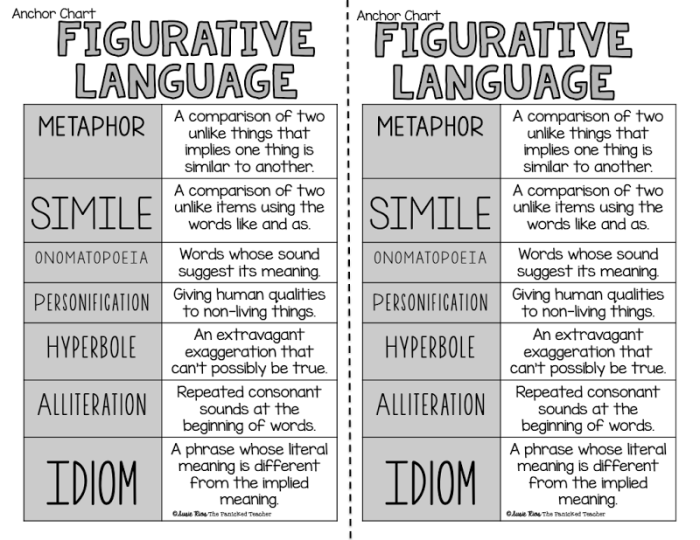
Figurative language is a literary device that uses words in a non-literal way to create a vivid image or make a point. It is used in all forms of literature, from poetry to prose, and can be a powerful tool for conveying meaning and emotion.
Simile
A simile is a figure of speech that compares two things using the words “like” or “as.” For example, “Her eyes were like sparkling diamonds.” Similes are used to create vivid imagery and to make a point by showing the similarities between two things.
Metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two things without using the words “like” or “as.” For example, “Her eyes were sparkling diamonds.” Metaphors are used to create a deeper meaning and to show the connection between two things.
Personification, Types of figurative language chart
Personification is a figure of speech that gives human qualities to non-human things. For example, “The wind whispered through the trees.” Personification is used to create a more vivid image and to make a point by showing the similarities between two things.
Hyperbole
Hyperbole is a figure of speech that exaggerates something for emphasis. For example, “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.” Hyperboles are used to create a humorous effect or to make a point by showing the extreme nature of something.
Irony
Irony is a figure of speech that uses words to convey a meaning that is the opposite of what is literally stated. For example, “It’s a nice day, isn’t it?” when it is actually raining. Irony is used to create a humorous effect or to make a point by showing the difference between what is said and what is meant.
Figurative Language Chart
| Type of Figurative Language | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Simile | Her eyes were like sparkling diamonds. | Compares two things using the words “like” or “as” to create vivid imagery. |
| Metaphor | Her eyes were sparkling diamonds. | Compares two things without using the words “like” or “as” to create a deeper meaning. |
| Personification | The wind whispered through the trees. | Gives human qualities to non-human things to create a more vivid image. |
| Hyperbole | I’m so hungry I could eat a horse. | Exaggerates something for emphasis to create a humorous effect or make a point. |
| Irony | It’s a nice day, isn’t it? (when it is raining) | Uses words to convey a meaning that is the opposite of what is literally stated to create a humorous effect or make a point. |
FAQs
What is the purpose of figurative language?
Figurative language allows writers to express complex ideas and emotions in a vivid and engaging way, enhancing the impact and memorability of their writing.
How can I use figurative language effectively in my writing?
To use figurative language effectively, choose specific and appropriate types that align with your desired tone and purpose. Ensure that the figurative language enhances your message rather than distracting from it.