Lab 12 the skeletal system joints answer key – Embark on an educational journey with Lab 12: The Skeletal System Joints Answer Key, an indispensable guide that unlocks the mysteries of the human skeletal system. Delve into the intricacies of joints, their functions, and classifications, gaining a comprehensive understanding of this vital body structure.
Through a step-by-step exploration of the lab’s activities, this answer key provides clarity and justification for each correct answer. Common misconceptions and errors are addressed, ensuring a thorough grasp of the subject matter. Moreover, additional resources and project ideas extend your learning beyond the lab, fostering a deeper appreciation for the significance of the skeletal system in our daily lives.
Introduction

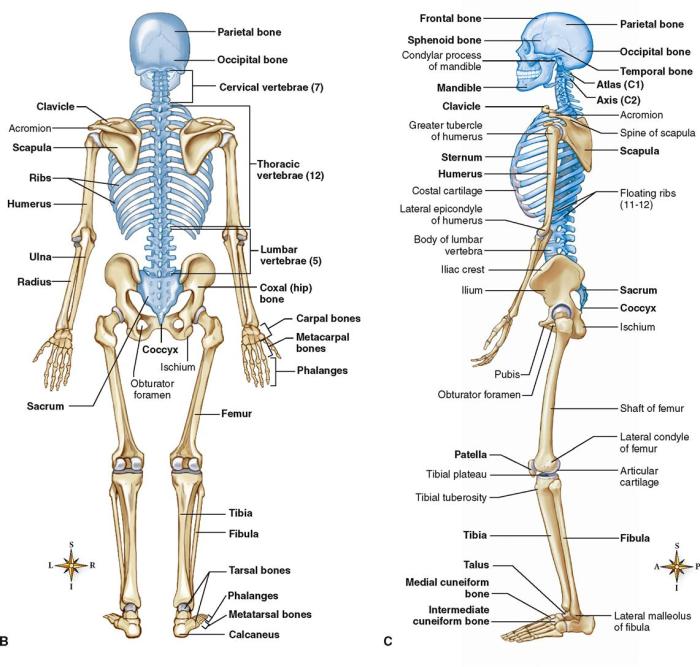
The skeletal system is a complex and dynamic system of bones, joints, and cartilage that provides support, protection, and movement for the body. It is composed of 206 bones, which are connected by joints to form a framework that supports the body and allows for movement.
The skeletal system has several important functions, including:
- Providing support for the body and its organs
- Protecting vital organs, such as the brain, heart, and lungs
- Facilitating movement through the contraction of muscles attached to bones
- Storing minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus
- Producing blood cells in the bone marrow
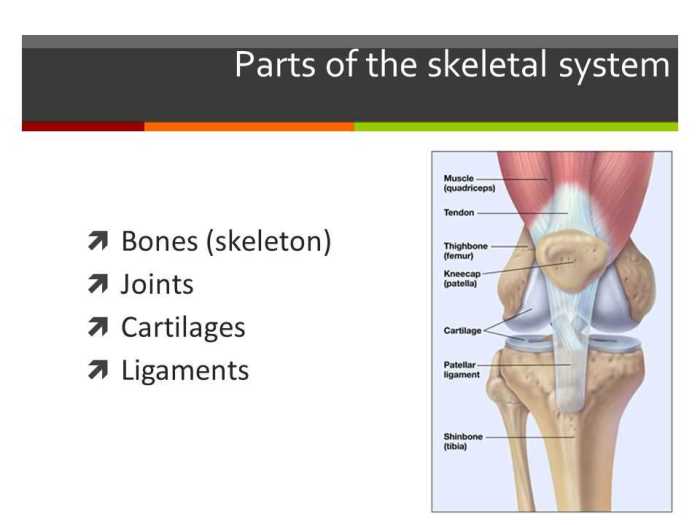
Joints
A joint is a point of contact between two or more bones. Joints allow for movement and provide stability to the skeletal system. There are three main types of joints:
- Fibrous joints: These joints are held together by fibrous tissue and allow for little to no movement. Examples of fibrous joints include the sutures between the bones of the skull and the syndesmoses between the bones of the forearm.
- Cartilaginous joints: These joints are held together by cartilage and allow for some movement. Examples of cartilaginous joints include the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae and the menisci in the knee.
- Synovial joints: These joints are the most common type of joint in the body. They are characterized by a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid, which provides lubrication and nourishment to the joint. Examples of synovial joints include the knee, hip, and shoulder joints.
Lab 12: The Skeletal System Joints
Purpose:The purpose of Lab 12 is to identify and classify the different types of joints in the human body.
Objectives:Upon completion of this lab, students will be able to:
- Identify the different types of joints in the human body
- Classify joints based on their structure and function
- Describe the range of motion of different types of joints
Materials:
- Human skeleton
- Joint model
- Dissecting kit
Procedure:
- Examine the human skeleton and identify the different types of joints.
- Use the joint model to demonstrate the range of motion of different types of joints.
- Dissect a joint to observe its structure.
Answer Key: Lab 12 The Skeletal System Joints Answer Key
1. What are the three main types of joints?
Fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints.
2. What is the difference between a fibrous joint and a cartilaginous joint?
Fibrous joints are held together by fibrous tissue and allow for little to no movement, while cartilaginous joints are held together by cartilage and allow for some movement.
3. What is the most common type of joint in the body?
Synovial joints.
4. What is the function of synovial fluid?
To provide lubrication and nourishment to the joint.
Popular Questions
What is the purpose of a synovial joint?
Synovial joints allow for smooth and flexible movement between bones, providing a wide range of motion.
How many types of cartilaginous joints are there?
There are three types of cartilaginous joints: synchondroses, symphyses, and intervertebral discs.
What is the difference between a ligament and a tendon?
Ligaments connect bones to bones, while tendons connect muscles to bones.
