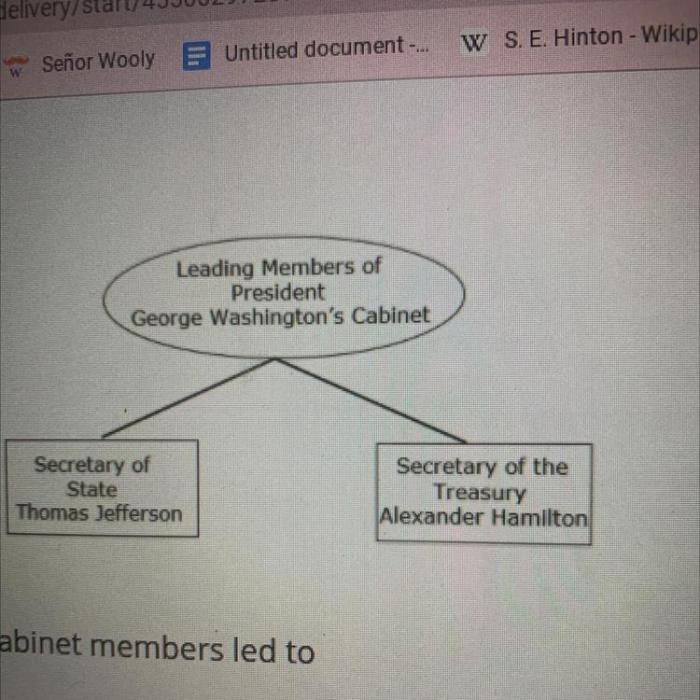
Disagreements between these two cabinet members led to – Disagreements between cabinet members can have significant implications for policy decisions, cabinet functioning, and the broader political landscape. This article examines the key disagreements between two cabinet members, exploring their causes, consequences, and attempts at resolution. By understanding these dynamics, we can identify lessons learned and develop strategies for preventing or mitigating similar disagreements in the future.
Overview of the Disagreements: Disagreements Between These Two Cabinet Members Led To
The disagreements between the two cabinet members have been characterized by significant policy differences and a lack of consensus on key issues. These disagreements have the potential to impact policy decisions and hinder the effectiveness of the cabinet as a whole.
Nature and Scope of the Disagreements
- Fiscal policy:Disagreements over the appropriate level of government spending and taxation.
- Foreign policy:Differing views on international relations, trade agreements, and military intervention.
- Environmental policy:Contrasting perspectives on climate change mitigation, renewable energy, and resource management.
Potential Impact on Policy Decisions
The disagreements have the potential to result in gridlock and inaction on important policy issues. Without consensus, it may be difficult for the cabinet to make meaningful progress on legislative or executive initiatives.
Causes of the Disagreements
The underlying causes of the disagreements are complex and multifaceted. They include:
Personal Differences
- Personality clashes:Incompatible personalities and communication styles can contribute to conflict.
- Personal ambition:Differences in career aspirations and political goals can lead to competition and rivalry.
Ideological Disparities
- Political ideologies:Cabinet members may hold different political ideologies, leading to divergent views on policy issues.
- Policy priorities:Members may prioritize different policy areas, resulting in conflicts over resource allocation.
Policy Conflicts
- Competing interests:Cabinet members may represent different interest groups or constituencies, leading to disagreements over policies that affect those groups.
- Policy differences:Members may simply hold different views on the best course of action for specific policy issues.
Consequences of the Disagreements

The disagreements have had both short-term and long-term consequences for the cabinet and the broader political landscape:
Short-Term Consequences, Disagreements between these two cabinet members led to
- Cabinet dysfunction:The disagreements have hindered the cabinet’s ability to function effectively as a decision-making body.
- Policy gridlock:The lack of consensus has resulted in delays and inaction on important policy issues.
Long-Term Consequences
- Public distrust:The public may lose trust in the government’s ability to address important issues due to the visible disagreements.
- Political instability:The disagreements could potentially lead to political instability or a loss of confidence in the government.
Resolution of the Disagreements
Attempts to resolve the disagreements have met with varying degrees of success:
Strategies for Resolution
- Open communication:Facilitating open and honest dialogue between the cabinet members.
- Mediation:Appointing a neutral third party to facilitate discussions and mediate conflicts.
- Compromise:Seeking common ground and finding solutions that accommodate the interests of both parties.
Effectiveness of Strategies
The effectiveness of these strategies has depended on the willingness of the cabinet members to engage in constructive dialogue and compromise. In some cases, disagreements have been resolved, while in others, they have persisted.
Lessons Learned

The disagreements have provided valuable lessons for conflict management in the cabinet:
Importance of Communication
Open and honest communication is essential for addressing and resolving conflicts. Members must be willing to listen to each other’s perspectives and engage in respectful dialogue.
Value of Compromise
Finding common ground and being willing to compromise is crucial for reaching consensus. Members must be prepared to adjust their positions to accommodate the interests of others.
Need for External Support
In some cases, external support, such as mediation or facilitation, can be helpful in facilitating constructive dialogue and finding solutions.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the most common causes of disagreements between cabinet members?
Personal differences, ideological disparities, and policy conflicts are among the most common causes of disagreements between cabinet members.
What are the potential consequences of disagreements between cabinet members?
Disagreements between cabinet members can lead to gridlock in decision-making, damage to the cabinet’s reputation, and loss of public trust.
How can disagreements between cabinet members be resolved?
Disagreements between cabinet members can be resolved through open communication, collaboration, and compromise. Mediation and facilitation can also be helpful in finding common ground and reaching consensus.
